Combustion processes are impossible without a high-functioning ignition system. And the CDI box (short for Capacitor Discharge Ignition) is among the most critical elements to keep that ignition system in check – yet beginners still stay alarmingly clueless about its mechanism.
Our article can help alleviate all confusion by diving into what a CDI on a motorcycle is. Keep scrolling.
Table of Contents
What Is A Motorcycle CDI Box? What Does It Do?
“CDI boxes” (Capacitor Discharge Ignition) control your bike’s ignition system using capacitors. Capacitors can store energy and release that power instantly and rapidly to create a high-voltage pulse and ignite the spark plug.
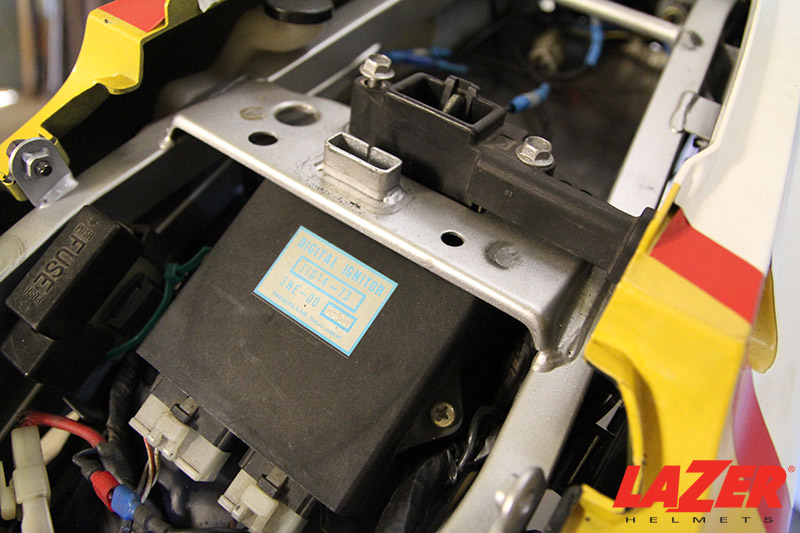
Specifically, the box serves as the bike’s trigger mechanism, whose encompassed components (capacitors, coils, and internal circuits) work together to speed up your ignition process. It goes through four major activation phases:
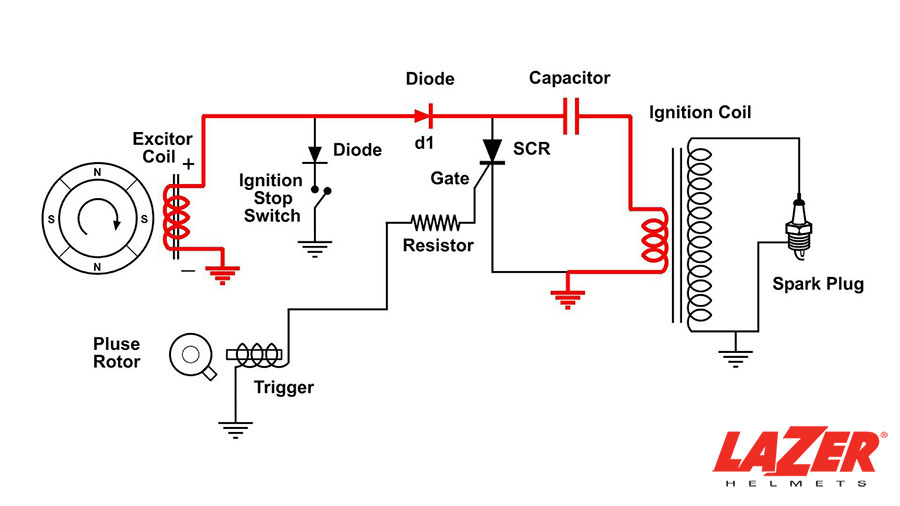
- The stator (a very important element of the electrical system) sends pulse signals to your CDI box as input.
- Your CDI box analyzes this input through various parameters (sensors, throttle position, engine speed, etc.) to determine the perfect timing for spark plug ignition.
- Once the math has been performed, the CDI sends pulse signals to the bike’s ignition coil to trigger the latter, which generates the required high-volt currents that ignite the fuel-air mixture inside the engine cylinder.
- The resulting sparks activate your bike’s combustion process, paving the way for a smooth and proper engine start.
What Causes A CDI Box To Fail?
The CDI box will go wrong if it undergoes a lot of abuse, like over-/under-voltage, water damage, overheating, excess vibration, or age. Electronic parts like this box can’t suffer from too much beating.
Any rider should have seen it coming: after all, no black boxes are invincible against heat, vibrations, and external damage.
CDI troubles with higher-end motorbikes are quite a rare sight, but that does not mean they are completely off the hook or impossible to happen. Failure to treat these problems on time might result in smokes, component blowouts, or even a complete breakdown of the entire igniter box (which costs quite a fortune to replace, by the way).
What Are Symptoms Of A Bad CDI Box?
Backfiring, misfired engines, rough start-ups, engine stalls, dead cylinders, and other ignition issues are some symptoms of a defective CDI box. They are quite easy to recognize (or, more like, impossible to ignore), even for beginners.
Below are 3 most common signs:
1. Backfiring

Backfiring (which refers to explosive, sudden fuel combustions within exhaust or intake systems), coupled with the banging, loud popping sounds, are among the most telltale symptoms of CDI malfunctions. You will find it much more prominent at high RPMs – above 3000, for instance.
Why is this symptom manifested? Simple: as mentioned, CDI boxes help determine the right ignition timing for your spark plugs. When the boxes fail to operate, your ignition coil will receive inconsistent voltage and false signals. Mistimed sparks and backfires are only to be expected.
2. Dead Cylinders
Failure to properly fire will rob the cylinders of their power output, so do not be surprised if there is (at least) one dead cylinder inside your engine chamber.
Defective forward/blocking diodes inside the CDI is the most likely culprit for the symptom.
In normal conditions, these diodes take charge of voltage signal regulations to ensure consistency and transparency. So when they stop working or become faulty, the signals will become erratic/fuzzy, confusing your spark plug’s firing mechanism.
3. Misfiring Engines

Misfiring engines also stem from faulty CDI boxes in serious cases.
However, CDI problems are only one among many potential reasons. Telling them apart would be impossible for beginners, so it is best to count on professional mechanic assistance in this case.
How To Troubleshoot and Diagnose A Malfunctioning CDI System?
Multimeters are among the most trusted and reliable troubleshooting tools for the CDI motorcycle wiring diagram. Use it to measure the resistance points of multiple CDI compartments, such as the wires, the pickup coils, and the HT coils.
1. Using Multimeters for The Blue and White Wires:
The guide below will detail how to test CDI box with multimeter using the blue and white wires:
Step one. Move the box off your bike.
The box is often installed below the bike’s seat. Plus, with the white/blue wire systems that connect it with the stator via pin and lead connectors, this box is impossible to miss.
Once disconnecting the box, give the CDI box 30 to 60 minutes to let the internal capacitors discharge. During the waiting time, it is time to carry on with your CDI visual inspections and identify physical deformations (if there are any).
Step two. Run a CDI cold test.
“Cold tests” refer to the process of inspecting the box components and their continuity. You don’t need to do much in this step, really:
- Take out the multimeter.
- Set it to the “Continuity” setting.
- Test the consistency between the terminal and ground points of the CDI.
Any existing problem would trigger the multimeter to give off beeping sounds. Continuity problems often stem from the internal capacitor, Diode, or SCR; fix them immediately to return the box to its normal working condition.
Step three. Run a hot CDI test.
Skip Step 2 to jump straight to Step 3 if you hate disconnecting the box from your bike – or treat Step 3 as an additional precaution after finishing the cold tests. It’s all up to you!
The test involves the stator ends of the white and blue wires connected to the box. To carry it out:
Set the multimeter to 2K OHMS, then measure resistance points between the white and blue wires/the white wires and the ground.
- For blue-white wires: the reading should fluctuate between 77 and 86.
- For white wires and the ground: 360 to 491 is the usual norm
Any number outside the two ranges mentioned above points to faulty stators; seek professional help immediately.
2. Using Multimeters for The Coils:
- The HT coils: Use the guidelines above, but this time, measure the resistance levels of the CDI’s primary/secondary windings. The winding resistance should fluctuate around 0.4 to 1.8 OHMS (for primary) and 5000 to 15000 OHMS (for secondary).
- Pickup Coils: Likewise, measure the pickup coil resistance. The number range differs across motorcycles, though 100 to 500 OHMS seems to be the norm.
How Much Does It Cost to Fix A CDI Box?
CDI box repairs/replacements demand 30$ to 900$. The bike’s model, features, brand, and even the shop’s per-hour rate have a lot of weight over the total number, so it isn’t easy to land on just one exact answer.
You might consider repairing the box on your own to save cost. However, internal tinkering might be challenging for beginners or the inexperienced since the box is completely sealed.
Are CDI Boxes Interchangeable?
No, they are not. Bike models do not have the same power supply systems (some are run by high-volt sour coils, while others use batteries, for instance). Hence, you cannot just install a random CDI box on your bike and expect it to work smoothly; they must be 100% compatible.
Conclusion
CDI boxes can be quite a pain to repair and replace. Thankfully, their malfunction symptoms are as clear as day, allowing even the most clueless rider to diagnose the issue before things are too late.
So keep my troubleshooting/diagnosis guide in mind, and write to me if you still have questions.