Are you ready to dive into the world of dirt bikes? Whether you’re a seasoned rider or a newcomer to the off-road scene, understanding the differences between 2 stroke and 4 stroke dirt bikes is essential. These two engine types have distinct characteristics that can significantly impact your riding experience.
I have gathered the nuances of these two dirt bike types, comparing their design, performance, and maintenance requirements. Let’s uncover the unique features of each engine type and help you make an informed decision when choosing your next dirt bike adventure.
Table of Contents
What Is A 2-Stroke Dirt Bike?
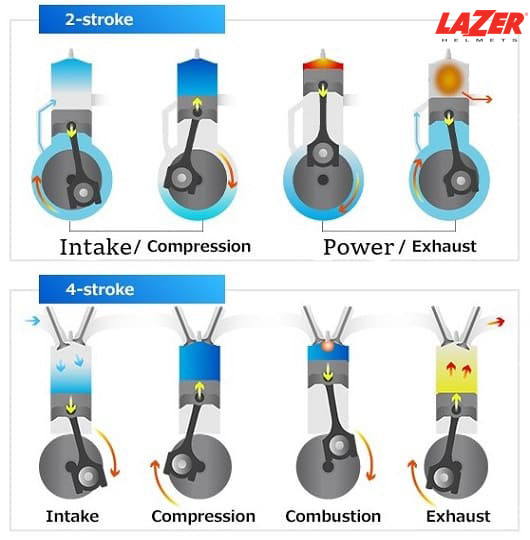
A 2-stroke motor completes a full power in just two strokes, where combustion and compression strokes take place at the same time, and the intake and exhaust of the gas also happens simultaneously. It gives riders more power and is best for off-road riding or racing.
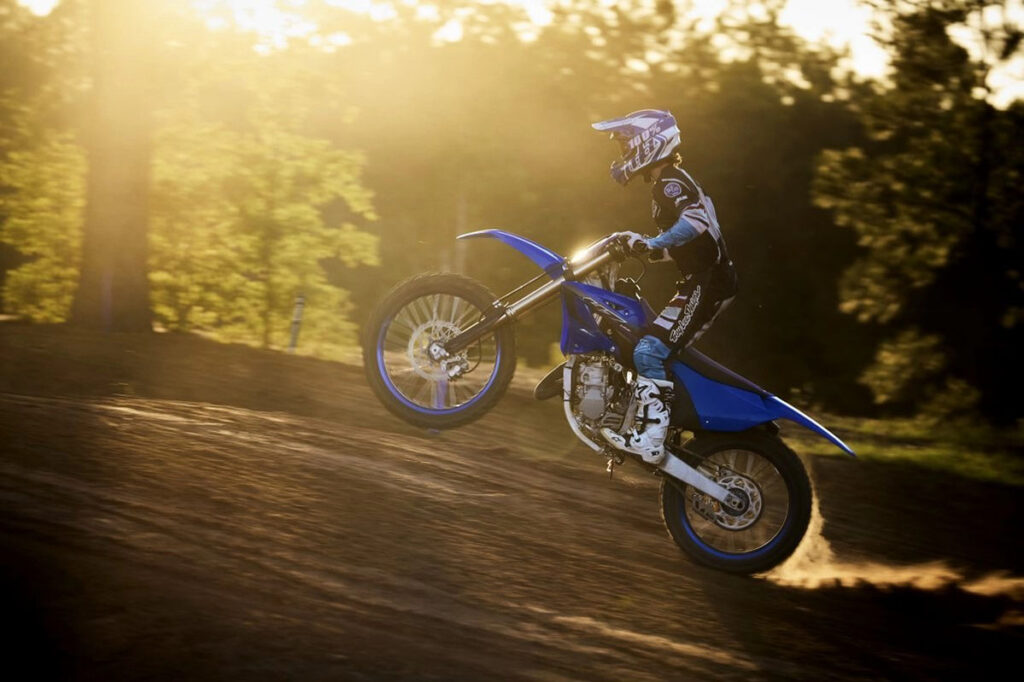

In a 2-stroke engine, the fuel and oil are mixed together before being injected into the combustion chamber. This mixture is ignited, creating an explosion that forces the piston downward, generating power. As the piston rises again, it pushes out the exhaust gas.
Pros
- Lightweight: 2-stroke dirt bikes tend to be lighter, making them easier to maneuver and handle.
- Power-to-weight ratio: Due to their design, 2-stroke engines can deliver more power in relation to their weight, making them capable of high speeds and quick acceleration.
- Simplicity: 2-stroke engines have a simpler design with fewer moving parts, leading to simpler maintenance and repair.
- Cost-effective: 2-stroke dirt bikes are often more affordable to purchase compared to 4-stroke models. They also tend to have lower maintenance costs.
- Intense powerband: 2-stroke engines have a unique power delivery characterized by a strong burst of power in the mid to high RPM (revolutions per minute) range, which can be exhilarating for riders who enjoy aggressive riding and racing.
Cons
- Fuel consumption: 2-stroke engines are less fuel-efficient, meaning they consume more fuel per mile. This can lead to more frequent refueling during rides.
- Emissions: 2-stroke engines produce higher levels of emissions compared to 4-stroke engines. They tend to generate more noise and emit more pollutants into the environment.
- Traction control: The intense powerband of 2-stroke engines can make it more challenging to maintain traction, especially in slippery or low-traction conditions. This can require more skill and control from the rider.
- Engine maintenance: While 2-stroke engines are generally simpler to maintain, they may require more frequent maintenance intervals, such as more frequent top-end rebuilds and spark plug replacements, due to the high RPM nature of the engine.
What Is A 4-Stroke Dirt Bike?
A 4-stroke dirt bike operates through a series of four distinct strokes to complete a power cycle: from intake to compression, power, and finally exhaust. The piston will drive the crankshaft in the power stroke to generate power and repeat until the engine stops running.
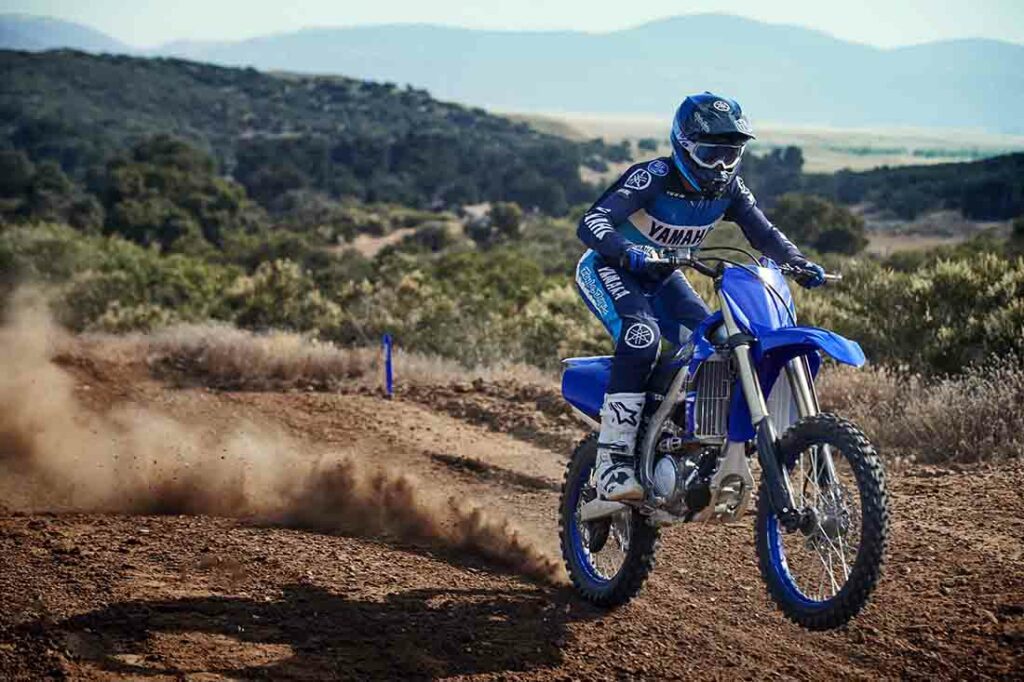

More specifically, in the first stroke – (intake), the piston goes downward, creating a vacuum that draws a fuel-air mixture into the cylinder. In the second stroke (compression), the piston will move up, compressing the mixture to increase its combustibility.
The power stroke is initiated by the spark plug. It ignites the compressed mixture, generates a controlled explosion that moves the piston downward and converts the linear motion into rotary motion through the crankshaft. Finally, in the exhaust stroke, the piston goes up again, releasing the burned gas via the exhaust valve and out of the engine.
Four-stroke engines have advanced significantly in recent years. This indicates that they are more effective and lighter than they once were. Four-stroke dirt bikes today have stronger power-to-weight ratios than they had in the past. A four-stroke engine is unable to match a two-stroke engine in terms of power, despite all the developments.

Pros
- Smooth power delivery: 4-stroke engines provide a smoother, more linear power delivery. This allows for better control and traction, especially in technical or slippery terrain.
- Fuel efficiency: They extract more power from each combustion cycle, resulting in longer riding times between refueling.
- Lower emissions: 4-stroke engines produce lower levels of exhaust emissions. They are designed to be more environmentally friendly, emitting fewer pollutants into the atmosphere.
- Low-end torque: They have more low-end torque, providing better acceleration and power at lower RPMs. This can be advantageous when climbing hills or maneuvering through challenging off-road conditions.
- Reduced maintenance: 4-stroke engines require less frequent maintenance. They often have longer service intervals for top-end rebuilds and spark plug replacements, resulting in lower maintenance costs and less downtime.
Cons
- Weight: 4-stroke dirt bikes tend to be quite heavy due to their more complex design and additional components, which can make them slightly less maneuverable and agile.
- Cost: The higher price can be attributed to the more intricate engine design and other parts.
- Complexity: 4-stroke engines have a more complex structure with more moving parts, which can make them more challenging to maintain and repair.
Which Is Better: 2-Stroke Or 4-Stroke?
The choice boils down to your needs. 2-stroke engines are simpler, lighter, faster, and more powerful but consume more fuel and release more emissions, best for racing and high-performance riding. 4-stroke engines are heavier and less powerful but low-maintenance and more fuel-efficient.
Performance
2-stroke engines are known for their lightweight and aggressive power delivery. They excel in delivering quick acceleration, making them popular among riders who seek thrilling bursts of power and high-speed performance.
On the other hand, 4-stroke ones provide a more controlled and predictable power delivery. They offer better low-end torque, allowing for smoother and more precise maneuvering. 4-strokes are favored by riders who value a more linear powerband and the ability to maintain traction in challenging conditions.
I can see this difference applies to two of my bikes. One is the KTM 300 EXC, and the other is the Honda CRF450R. The former, with a 300cc 2-stroke engine, brings a strong power delivery with excellent torque whenever I rev up. Its agility and responsiveness make it well-suited for technical off-road trails and high-speed riding.
Meanwhile, the latter, which comes with a 450cc 4-stroke engine, offers steady acceleration with little to no abruptions.
So a 4-stroke bike, with its responsive throttle and smooth power delivery, will enable riders to modulate their acceleration, ensuring precise control when entering and exiting turns.
Weight
Generally, 2-stroke engines tend to be lighter than their 4-stroke counterparts. The weight gap might be different among models.
For example, the 2-stroke engine of the 2023 KTM 250 XC dirt bike weighs around 52.6 pounds, while a 2023 KTM 250 SX-F 4-stroke dirt bike may weigh around 57.6 pounds. The simplicity of their design and fewer moving parts contribute to reduced overall weight.
Additionally, these machines do not require some of the heavier components found in their counterparts, such as camshafts, valves, and a separate oil system. This lighter weight provides benefits in terms of maneuverability and agility, allowing riders to navigate tight corners and challenging terrain with greater ease.
However, technology advancements have resulted in lighter 4-stroke engines in recent years, narrowing the weight gap between the two types. Thus, the difference might not be as obvious now.
Durability
When it comes to durability, 4-stroke engines generally have an advantage over 2-stroke engines. The design of 4-stroke engines includes a separate lubrication system for engine oil, which helps reduce wear and tear on internal components.
This can result in increased longevity and durability, especially when compared to the higher RPM nature of 2-stroke engines. Additionally, 4-stroke engines often have longer service intervals for maintenance, meaning less frequent rebuilds and part replacements.
2-stroke engines have a simpler design with fewer moving parts, making them more lightweight and less prone to certain types of mechanical failures. However, they often require more frequent maintenance and may need component replacements, such as piston rings, more frequently.
Fuel Consumption
4-stroke engines are known for their superior fuel efficiency, extracting more power from each combustion cycle. This results in longer riding times between refueling, making them an ideal choice for longer rides, endurance races, or situations where access to fuel stations may be limited.
2-stroke ones typically consume more fuel due to their higher RPM nature and the need for oil mixed with fuel for lubrication. The oil in the fuel mixture can contribute to higher fuel consumption.
Still, it’s worth noting that advancements in 2-stroke technology, such as direct injection systems, have helped improve fuel efficiency in some newer 2-stroke models, like the KTM 250 EXC TPI or Husqvarna TE 300i.
Emission
4-stroke engines have a more advanced design that includes separate intake and exhaust strokes, allowing for more efficient combustion. This results in lower levels of exhaust emissions, as the fuel is burned more completely.
2-stroke engines, on the flip side, tend to produce higher emissions rates due to their design, where the fuel-air mixture is both ingested and exhausted in the same stroke. It can lead to incomplete combustion, releasing harmful pollutants into the air, such as hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides.
These emissions can include unburned fuel and lubricating oil, contributing to higher levels of air pollution. As a result, many countries and regions have implemented stricter emission regulations, favoring the use of 4-stroke engines.
In reality, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has set stricter emission standards for motorcycles, which has led to the decline of two-stroke bikes. In the United States, new two-stroke motorcycles are no longer legal to sell.
Noise Level
When it comes to noise level, 4-stroke engines gain the upper hand compared to their counterparts. 4-stroke ones operate with a more muffled exhaust note due to their design, which includes separate exhaust and intake strokes.
This results in a quieter running engine compared to the distinct high-pitched sound produced by 2-stroke engines. The more controlled and refined combustion process of 4-strokes contributes to reduced noise levels, making them a preferred choice for riders who value a quieter riding experience.
As with my KTM 300 EXC, I’d said it could be heard from over a mile away. I have figured out why 2-stroke bikes are louder.
First, these motors have no valves. This means the fuel and air mixture is not evenly distributed throughout the cylinder, creating more noise. Second, they have no oil separation system. As the oil and fuel are mixed together, it results in incomplete combustion and louder noise.
Maintenance Requirement
2-stroke engines tend to have a simpler design with fewer moving parts, making them easier to maintain and repair. However, due to their higher RPM nature, they often require more frequent maintenance intervals, such as top-end rebuilds and spark plug replacements.
On the flip side, 4-stroke engines have a more complex design with additional components, but they often have longer service intervals. This means less frequent maintenance and lower overall maintenance costs. Additionally, 4-stroke engines typically have separate oil and fuel systems, simplifying maintenance and reducing the need for mixing oil with fuel as required in 2-stroke engines.
Summary
As mentioned, the “better” choice between 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines depends on your needs, riding style, and preferences. Consider factors such as power characteristics, fuel efficiency, maintenance requirements, and emission regulations when making a decision. I have made a complete comparison table so you can see the differences better.
| 2-Stroke | 4-Stroke | |
| Size Of Engine | Smaller | Larger |
| Engine Power | Higher power per cubic | Lower power per cubic |
| Horsepower | More horsepower | Less horsepower |
| Starting | Quicker start | Slower start |
| Maintenance | Require more maintenance but easier and cheaper | Less maintenance but slightly more complicated and costly |
| Noise | Louder | Quieter |
| Cost | Cheaper | More expensive |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
| Terrain | Suitable for technical terrains | Suitable for open-high speed terrain |
| Parts | Less moving parts | More moving parts |
| Vibration | More vibrations | Fewer vibrations |
Frequently Asked Questions
Do 4-Stroke Engines Need Oil?
Yes. Unlike 2-stroke engines, which mix oil with fuel for lubrication, 4-stroke engines have a separate oil system. The oil circulates within the engine, lubricating components such as the piston, crankshaft, and valves. Regular oil changes and maintenance are necessary to ensure the longevity and smooth operation of a 4-stroke engine.
Why Are 2-Strokes Cheaper Than 4 Strokes?
Two-stroke engines are often cheaper than four-stroke engines due to their simpler design with fewer moving parts. The manufacturing process for two-stroke engines is generally less complex, resulting in lower production costs. Also, two-stroke machines are lighter and require fewer materials, further contributing to cost savings.
Can You Turn A 4-Stroke Into A 2 Stroke?
No. The design, mechanics, and combustion processes of the two engines are fundamentally different. Converting an engine from one type to another would require significant modifications to the internal components, fuel delivery system, and exhaust system, which would be highly impractical and technically challenging.
The Bottom Line
Choosing between a dirt bike engine 2 stroke and 4-stroke comes down to your personal needs. Both engine types offer unique advantages and considerations.
Whether you prioritize speed, torque, maintenance ease, or environmental impact, understanding the differences between these two engine types will help you make an informed decision and find the perfect dirt bike that aligns with your riding aspirations.









